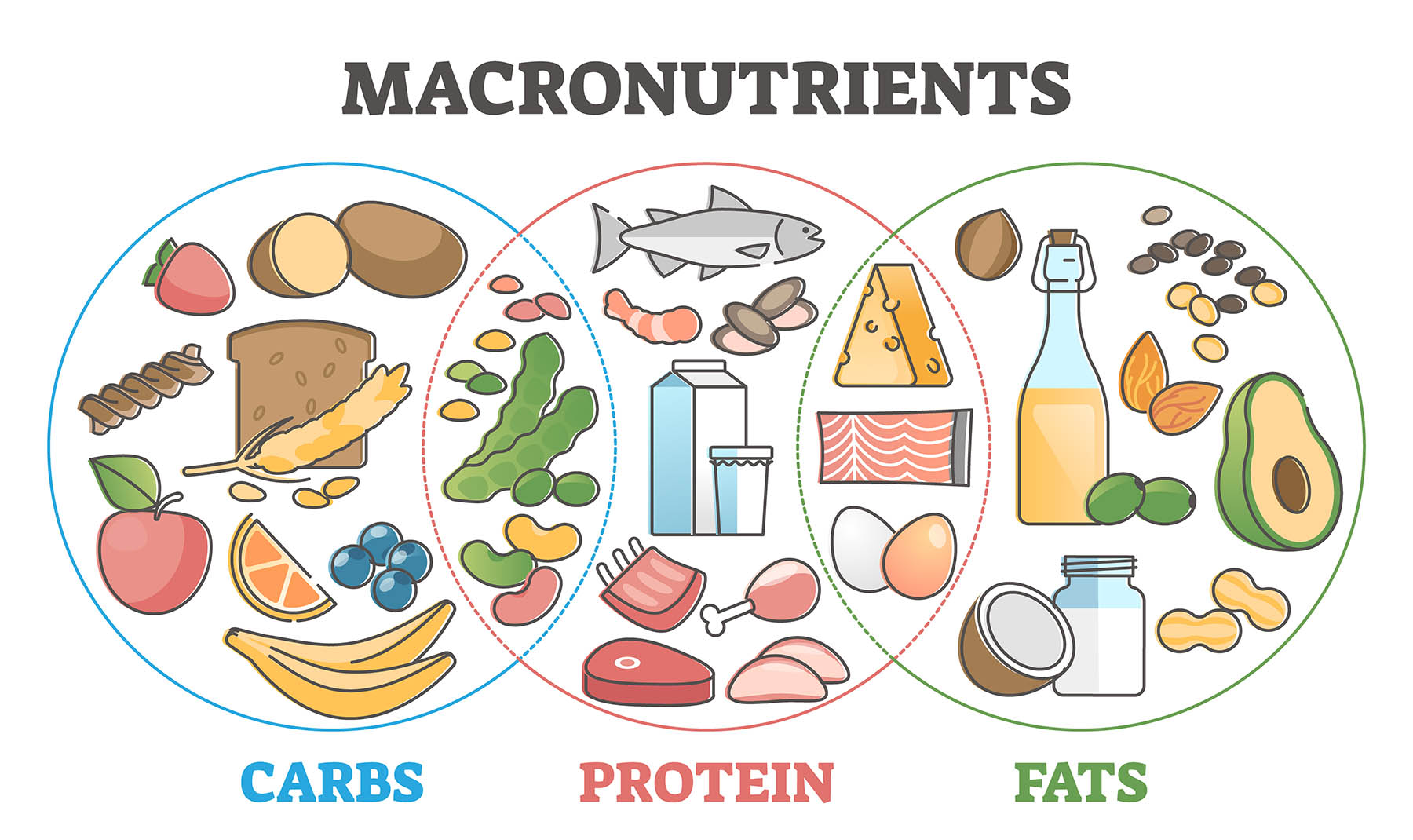
Why Macronutrients Matter
Macronutrients are the primary nutrients our bodies require in substantial amounts for optimal function. Not only do they serve as our primary energy source, but they also play diverse and significant roles in various bodily processes. From repairing cells to facilitating metabolic reactions and providing structure to our cells, these nutrients are indispensable. A balanced intake of macronutrients ensures the proper functioning of the cardiovascular, muscular, nervous, and skeletal systems. Furthermore, by understanding the specific role and significance of each macronutrient, we empower ourselves to make informed dietary choices that bolster overall well-being.
The Power of Protein
Proteins are intricate molecules that play a pivotal role in virtually all biological processes. Often referred to as the building blocks of life, proteins are imperative for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. They consist of chains of amino acids, some of which are essential, meaning the body can’t produce them and must obtain them from food. Apart from tissue repair, proteins are instrumental in enzyme and hormone production, which mediate metabolic reactions and maintain cellular functionality. They also play a crucial role in supporting a robust immune system, transporting molecules, and ensuring the proper functioning of our blood. Sources: Rich sources include lean meats like chicken and turkey, dairy products, eggs, legumes like beans and lentils, nuts, seeds, and soy products.
Fats: Not the Enemy
Fats, though often vilified in popular media, are a dietary cornerstone. They are dense energy sources, providing 9 calories per gram, making them vital for high-energy demands. Fats have numerous roles in the body, from acting as an energy reserve to supporting cellular growth and development. They also play a role in protecting our vital organs from shock and temperature changes. Furthermore, fats are instrumental in the production of essential fatty acids and hormones, and they assist in the absorption of certain vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. Types and Sources: Saturated Fats are mainly found in animal products like red meat, butter, and cheese. Unsaturated Fats are predominant in plant sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts. Trans Fats, which should be limited due to health concerns, are typically found in some processed foods.
Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are primarily known as the body’s go-to energy source. When consumed, they are broken down into simpler sugars, with glucose being the most common. This glucose is then used by our cells for energy or stored for later use. Carbohydrates are especially vital for high-intensity physical activity and proper brain function. They also play a role in various metabolic processes and can influence mood and memory. Beyond energy provision, certain types of carbohydrates, like dietary fiber, play a role in digestive health, assisting in waste elimination and promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Types: Simple Carbohydrates offer quick energy and are found in fruits, dairy products, and sugar-sweetened foods. Complex Carbohydrates provide sustained energy due to their longer chain structures and are found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
Balancing Macronutrients for Optimal Health
Achieving a balance in macronutrient intake is paramount for overall health. Each person’s ideal balance might differ based on several factors, including age, metabolic rate, activity level, and specific health goals. While there are general dietary guidelines, it’s essential to remember that individual needs can vary widely. It’s not just about quantity, but quality matters too. Prioritizing whole foods and minimizing processed food intake can significantly impact overall health. For a deeper understanding and personalized guidance, consulting with a nutritionist or dietitian is advisable.
Macronutrients and Fitness Goals
Depending on individual fitness and health objectives, the ratio and type of macronutrient intake might need adjustments. For example, individuals aiming for muscle growth might prioritize protein to support muscle repair and synthesis. Those focusing on endurance sports might lean towards higher carbohydrate intakes to ensure sustained energy levels. Understanding how to tweak macronutrient intake based on specific goals can significantly enhance performance and results.
Monitoring Macronutrient Intake
With today’s technological advancements, numerous tools and apps can help individuals track their daily macronutrient intake. These tools are particularly valuable for those with specific health goals, dietary restrictions, or those merely curious about their nutritional patterns. Monitoring can provide insights into any deficiencies or excesses, allowing for timely dietary adjustments. Regular tracking can lead to heightened nutritional awareness and better overall health outcomes.
Staying Informed and Adapting Your Approach
As you delve deeper into understanding macronutrients, it’s beneficial to stay updated with the latest research and findings. Nutritional science is ever-evolving, and what’s considered optimal today might change with new insights. Being adaptable and open to learning ensures that you’re always at the forefront of making the best dietary choices for your health and wellness journey. Remember, it’s a continuous journey of learning, adapting, and growing towards better health and well-being.